Sounding Rocket
Joachim Köppen Strasbourg/Kiel 2004/2013
Contents
The Applet simulates the flight of a sounding rocket through the Earth atmosphere, and permits to plot any variable of the flight (range, speed, acceleration, ...) as a function of time, or as a function of any of the other variables.
The rocket is composed of the rocket case and motor (the "dry mass"), the fuel, and the payload. It is launched into a certain angle into the air, the fuel is consumed at a constant rate for a certain time, after which the rocket continues to rise on a ballistic trajectory. During all that time, the resistance due to the air acts on the rocket, described by an effective cross section of the rocket. This will be smaller than the geometrical cross section, due to the aerodynamic shape. After some time, the payload is separated from the rocket, and descends to the ground while slowed down by the main parachute (whose braking is described by its effective cross section).
All parameters have simply been adjusted until a satisfactory match with the flight data of a Zuni mission was achieved. No claim for accuracy is made, and no warranty is given!
This software is designed as a graphical visualization only of typical missions.
The simulator solves the equation of motion, including thrust, gravity, and air friction, with a simple method using an adaptive time step width between 0.1 and 100 msec.
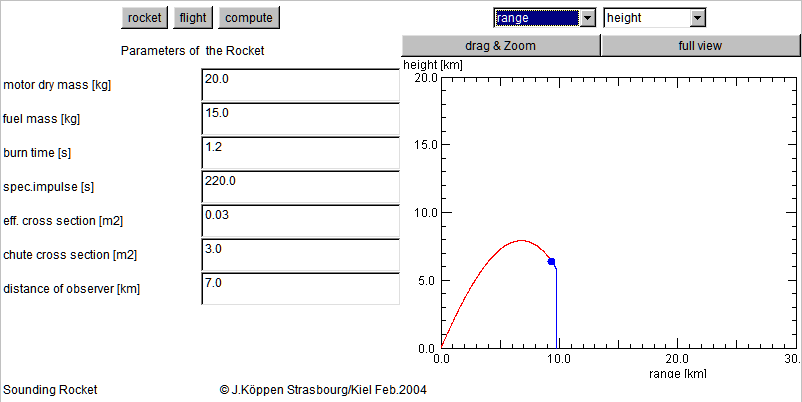
When you start up the applet, you shall see the plot of height versus range of a typical flight of a Zuni sounding rocket.

The red part shows the flight before separation, the blue one the flight of the payload under parachute. Change the x and y axes with the Choices in the upper right, to display the new plot. Use drag & Zoom to see more details. Change any of the parameters on the left hand side panels, and then hit the enter key or click compute to make and show the new simulation.
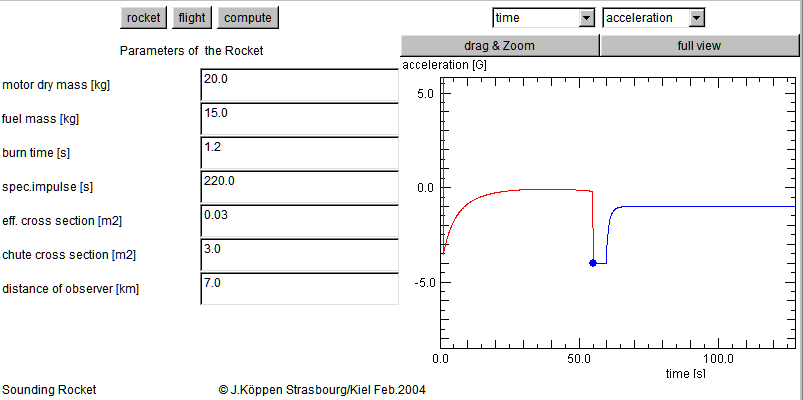
For instance, here we see that around the time of peak altitude there is a 30 second stretch of low acceleration (perhaps less than 0.1 G). Then the drogue chute opens and limits the acceleration to -4 G (my arbitrary assumption). When the payload is falling under the main parachute, the air drag on the chute amounts to 1 G.
| Top of the Page | Controls | Applet | Applet Index |